Unlocking Happiness: The Science of Feel-Good Hormones
- innovatewithstem12
- Oct 11, 2024
- 4 min read
Published on: October 11th, 2024
By: Miriam Kelton
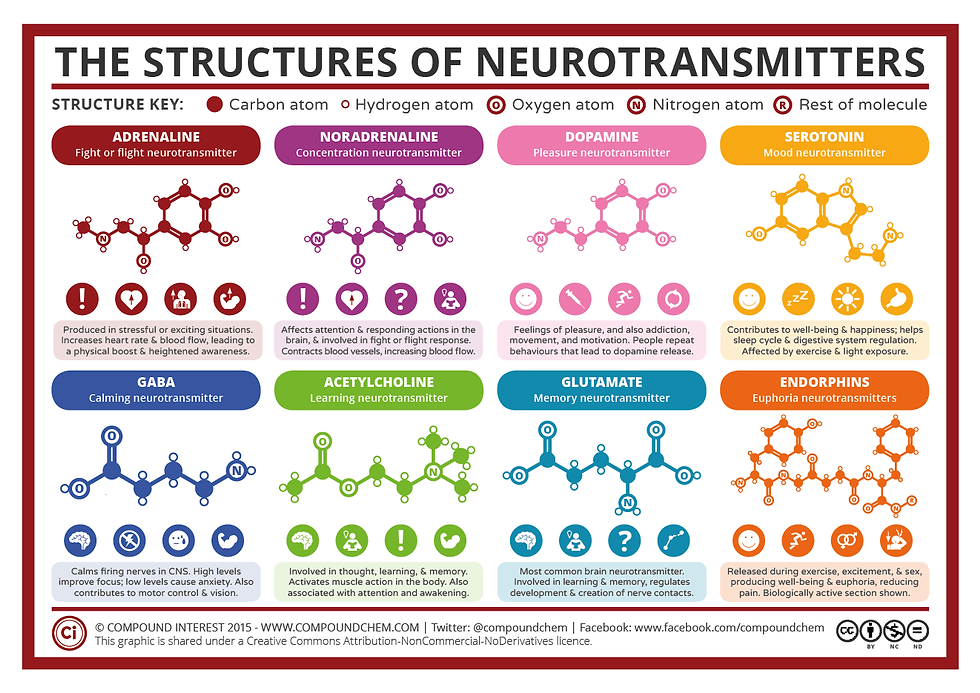
There is a group of four brain chemicals called the “feel-good hormones” due to the pleasure and euphoria they produce. Understanding how these chemicals work and impact our mood, behavior, stress, and social interactions is necessary for implementing positive changes and growth. These endogenous chemicals are neurotransmitters that act as chemical messengers by carrying information between synaptic cells. The sites at which neurons connect and exchange information are called synapses. These chemicals can also be released into the bloodstream through glands, changing how your body feels. Understanding these four chemicals and the small habits you can implement can make a huge difference in your mood and mental health.
(Weaver)
Do you know that tingling excitement and joy the smell of freshly baked cookies brings? This is just one of the many activities that can increase dopamine levels. Domaine is known as the reward chemical due to the intense pleasure rush it causes. Other enjoyable activities such as completing a task from our to-do list, self-care activities, eating our favourite food, and celebrating little wins contribute to rising dopamine levels. This affects the brain’s reward pathway which reinforces the desired behaviour. Tyrosine makes up dopamine; consuming food rich in tyrosine, such as poultry, dairy, and avocados may boost dopamine levels. Dopamine is closely linked to motivation so setting small, achievable goals can create a sense of accomplishment and encourage further efforts. Dopamine plays a large role in addiction due to the thrill of activities such as drinking, overeating and drugs. It can mislead our brains into believing these behaviors are healthy for us. While we can naturally boost dopamine levels and enhance our motivation in many ways, it is crucial to remain aware of the huge impact this powerful chemical can have.
We all know by now that life comes with ups and downs. This reality reinforces the importance of the chemical serotonin, the mood stabilizer. This neurotransmitter balances mood and feelings of happiness. Serotonin synthesis occurs in your brain and gut, connecting your physical and mental well-being. It helps regulate your mood, anxiety, and sleep patterns. This also means that low levels of this hormone are linked to mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression. A type of antidepressant, Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors or SSRIs, work to increase Serotonin levels. This can reduce symptoms such as feelings of overwhelming anxiety or panic attacks. You can enhance serotonin production by adding healthy habits such as meditating, running, morning sun exposure, walking, swimming, and cycling to boost your physical and mental health. When you ride your bike or lift weights, your body produces more tryptophan, which is the amino acid that your brain needs to create serotonin. Small, consistent efforts can drastically reduce stress and stabilize your mood and energy.
With great highs come great lows; this is why endorphins play an important role in our lives. Endorphins are peptides that act as a natural painkiller and help elevate mood. They act as our body’s natural response to alleviate discomfort during physical activity and stressful situations. This chemical binds to opioid receptors in our brain, which reduce our perceptions of pain and release euphoric feelings. This might be why you have heard of a “runner’s high," or the strong release of endorphins from strenuous aerobic exercises. Another way to stimulate endorphin release in your body is through stress management activities such as yoga, meditation, baths, listening to music, dark chocolate, and laughter. These activities can promote relaxation and joy, improving your emotional health. Remember that lows in life are just temporary, but if you are looking to reduce difficult emotions, try to make time for an endorphin-releasing activity to provide some temporary pain relief.
(Brunning)
The final of the four feel-good hormones is Oxytocin or "the love hormone.” It is released during emotional and bonding activities such as hugging, social interactions, exercise, childbirth, compliments, and playing with pets. This neurotransmitter helps foster social connections and trust, both necessary for a fulfilling and cheerful life. Furthermore, it plays a key role in reducing stress and anxiety by promoting feelings of security and comfort. If you strive to strengthen your emotional bonds, ensure you focus on activities that promote physical touch like a hug, kiss, or massage.
Overall, it is evident the impact these four neurotransmitters play on overall well-being and happiness. It is important to make time for activities that create a release of these powerful chemicals including exercise, self-care, and social interaction. I encourage you to brainstorm some of the practical applications and habits you can add to your everyday schedule based on what you have learned. Start implementing some of these little tasks and you may be surprised that the winter blues don’t hit you as hard this coming season.
Sources:
Brunning, Andy. “Compound Interest: A Simple Guide to Neurotransmitters.” Compound Interest: Chemistry infographics, 30 July 2015, https://www.compoundchem.com/2015/07/30/neurotransmitters/. Accessed 28 September 2024.
Sheffler, Zachary M., et al. “Physiology, Neurotransmitters - StatPearls.” NCBI, 1 May 2023, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539894/. Accessed 28 September 2024.
“The synapse (article) | Human biology.” Khan Academy, 2016, https://www.khanacademy.org/science/biology/human-biology/neuron-nervous-system/a/the-synapse. Accessed 28 September 2024.
Watson, Stephanie, and Howard E. LeWine. “Feel-good hormones: How they affect your mind, mood, and body.” Harvard Health, 18 April 2024,
https://www.health.harvard.edu/mind-and-mood/feel-good-hormones-how-they-affect-your-mind-mood-and-body. Accessed 27 September 2024.
Weaver, Elizabeth A. “Neurotransmission: Neurotransmitters.” Dana Foundation, 22 September 2023, https://dana.org/resources/neurotransmission-neurotransmitters/. Accessed 28 September 2024.






Comments